Effects of Bamboo Fiber Length and Loading on Mechanical, Thermal and Pulverization Properties of Phenolic Foam Composites
-
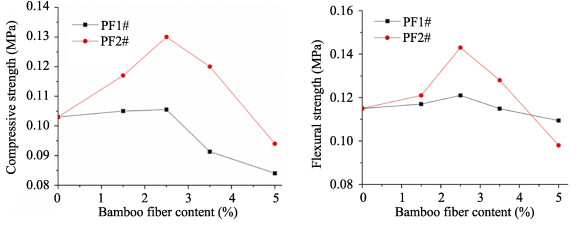
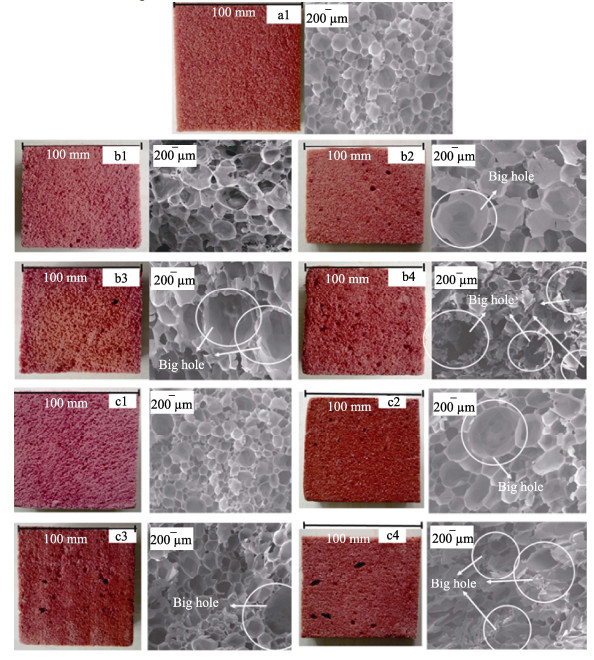
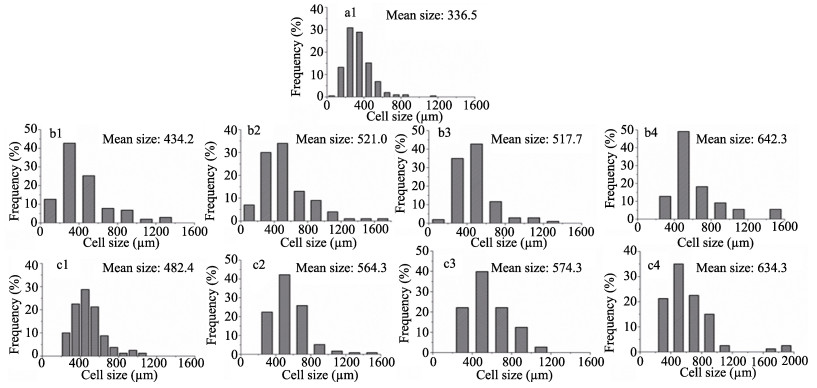
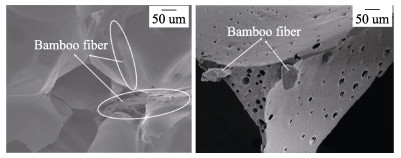
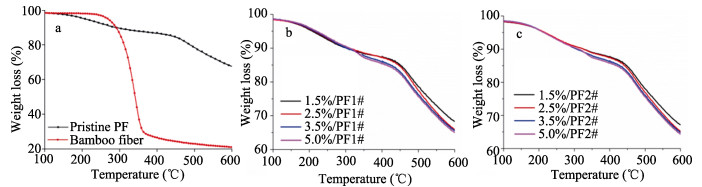
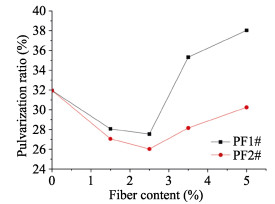
Abstract: In order to improve the mechanical properties and toughness of phenolic foams, a reinforcement method using two kinds of bamboo fibers was optimized with respect to the fiber contents. The compressive and flexural properties, thermal stability, friability and morphology of the phenolic foam composites were studied. The mechanical properties of the pristine foam and composites were evaluated by measuring the compressive strength. The results showed that the greatest mechanical properties were achieved by incorporating 2.5wt% of the reinforcement, and the compressive and flexural strengths of the two composites increased by 26.21% and 24.35%, respectively, compared with that of the pristine foam. The results of thermogravimetric testing demonstrated that the addition of bamboo fiber imparted better thermal stability to the phenolic foam, which was mainly attributed to the higher initial thermal decomposition temperature of the bamboo fiber. However, the influences of both reinforcements on the thermal stability of the material were negligible. The incorporation of bamboo fiber decreased the friability of the phenolic foam. Furthermore, the reduction in friability of the foam composites with longer lengths were higher than that in foams with shorter bamboo fibers. Moreover, the morphology and cell sizes of the fiber-reinforced phenolic foams were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy, the results indicated strong bonding between the fibers and phenolic matrix, and the incorporation of the bamboo fibers into the foam resulted in increased cell size of the material. Finally, the thermal conductivity and flame resistance of the phenolic foams reinforced by the bamboo fibers were also measured.
-
Key words:
- phenolic foam /
- bamboo fiber /
- composite /
- mechanical property /
- microstructure
-
Table 1. Compositions and characterizations of pristine foam and composites
Sample designation Foaming phenolic resin (g) Bamboo fibers mass fraction (%) Tween-80 (g) Catalyst (g) Foaming temperature (℃) Actual density (g/cm3) Pristine PF 100 0 0.3 10 60 0.030 1.5%/PF1# 100 1.5 0.3 10 60 0.031 2.5%/PF1# 100 2.5 0.3 10 80 0.033 3.5%/PF1# 100 3.5 0.3 10 100 0.031 5.0%/PF1# 100 5.0 0.3 10 110 0.029 1.5%/PF2# 100 1.5 0.3 10 60 0.030 2.5%/PF2# 100 2.5 0.3 10 80 0.028 3.5%/PF2# 100 3.5 0.3 10 110 0.029 5.0%/PF2# 100 5.0 0.3 10 120 0.031 Table 2. Thermal decomposition data of pristine foam, bamboo fibers and the foam composites
Sample designation T5% (℃) Residual yield at
600℃ (%)Bamboo fiber 268 21.1 Pristine PF 205 67.6 1.5%/PF1# 208 68.3 2.5%/PF1# 213 65.9 3.5%/PF1# 216 65.6 5.0%/PF1# 219 65.0 1.5%/PF2# 215 67.1 2.5%/PF2# 216 65.2 3.5%/PF2# 217 64.9 5.0%/PF2# 214 64.4 Note: T5% is defined as the sample temperature at 5% weight loss. -
Bo C Y, Wei S K, Hu L H, et al., 2016. Synthesis of a cardanol-based phosphorus-containing polyurethane prepolymer and its application in phenolic foams. RSC Advances, 6(67): 62999–63005. DOI: 10.1039/c6ra08249a. Choe J, Kim M, Kim J, et al., 2016. A microwave foaming method for fabricating glass fiber reinforced phenolic foam. Composite Structures, 152: 239–246. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.05.044. del Saz-orozco B, Oliet M, Alonso M V, et al., 2012. Formulation optimization of unreinforced and lignin nanoparticle- reinforced phenolic foams using an analysis of variance approach. Composites Science and Technology, 72(6): 667–674. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2012.01.013. del Saz-orozco B, Alonso M V, Oliet M, et al., 2014. Effects of formulation variables on density, compressive mechanical properties and morphology of wood flour-reinforced phenolic foams. Composites Part B: Engineering, 56: 546–552. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.08.078. del Saz-orozco B, Alonso M V, Oliet M, et al., 2015. Mechanical, thermal and morphological characterization of cellulose fiber-reinforced phenolic foams. Composites Part B: Engineering, 75: 367–372. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.01. 049. Ikeda R, Tanaka H, Uyama H, et al., 2002. Synthesis and curing behaviors of a crosslinkable polymer from cashew nut shell liquid. Polymer, 43(12): 3475–3481. DOI: 10.1016/ S0032-3861(02)00062-9. Lee S H, Wang S Q, 2006. Biodegradable polymers/bamboo fiber biocomposite with bio-based coupling agent. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 37(1): 80–91. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2005.04.015. Li Q L, Chen L, Zhang J J, et al., 2015. Enhanced mechanical properties, thermal stability of phenolic-formaldehyde foam/ silica nanocomposites via in situ polymerization. Polymer Engineering & Science, 55(12): 2783–2793. DOI: 10.1002/ pen.24169. Li Q L, Chen L, Li X H, et al., 2016. Effect of multi- walled carbon nanotubes on mechanical, thermal and electrical properties of phenolic foam via in-situ polymerization. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 82: 214–225. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.11.014. Li Z Q, Jiang Z H, Fei B, H et al., 2014. Comparison of bamboo green, timber and yellow in sulfite, sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide pretreatments for enzymatic saccharification. Bioresource Technology, 151: 91–99. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech. 2013.10.060. Liu L, Fu M T, Wang Z Z, 2015. Synthesis of boron-containing toughening agents and their application in phenolic foams. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 54(7): 1962–1970. DOI: 10.1021/ie504851y. Nahar S, Khan R A, Dey K, et al., 2012. Comparative studies of mechanical and interfacial properties between jute and bamboo fiber-reinforced polypropylene-based composites. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials, 25(1): 15–32. DOI: 10.1177/0892705711404725. Parameswaran P S, Bhuvaneswary M G, Thachil E T, 2009. Control of microvoids in resol phenolic resin using unsaturated polyester. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 113(2): 802–810. DOI: 10.1002/app.29667. Song S A, Chung Y S, Kim S S, 2014. The mechanical and thermal characteristics of phenolic foams reinforced with carbon nanoparticles. Composites Science and Technology, 103: 85–93. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2014.08. 013. Sukmawan R, Takagi H, Nakagaito A N, 2016. Strength evaluation of cross-ply green composite laminates reinforced by bamboo fiber. Composites Part B: Engineering, 84: 9–16. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.08.072. Yang C, Zhuang Z H, Yang Z G, 2014. Pulverized polyurethane foam particles reinforced rigid polyurethane foam and phenolic foam. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 131(1): 39734. DOI: 10.1002/app.39734. Yang Y F, He J M, 2015. Mechanical characterization of phenolic foams modified by short glass fibers and polyurethane prepolymer. Polymer Composites, 36(9): 1584–1589. DOI: 10.1002/pc.23066. Yang H Y, Wang X, Yu B, et al., 2013. A novel polyurethane prepolymer as toughening agent: Preparation, characterization, and its influence on mechanical and flame retardant properties of phenolic foam. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 128(5): 2720–2728. DOI: 10.1002/app.38399. Yang J N, Li P, 2015. Characterization of short glass fiber reinforced polypropylene foam composites with the effect of compatibilizers: A comparison. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites, 34(7): 534–546. DOI: 10.1177/ 0731684415574142. Yang Z J, Yuan L L, Gu Y Z, et al., 2013. Improvement in mechanical and thermal properties of phenolic foam reinforced with multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 130(3): 1479–1488. DOI: 10.1002/app. 39326. Yu Y, Wang H K, Lu F et al., 2014. Bamboo fibers for composite applications: a mechanical and morphological investigation. Journal of Materials Science, 49(6): 2559–2566. DOI: 10.1007/s10853-013-7951-z. Yuan H X, Xing W Y, Yang H Y, et al., 2013. Mechanical and thermal properties of phenolic/glass fiber foam modified with phosphorus-containing polyurethane prepolymer. Polymer International, 62(2): 273–279. DOI: 10.1002/pi.4296. Zhou J T, Yao Z J, Chen Y X, et al., 2013. Thermomechanical analyses of phenolic foam reinforced with glass fiber mat. Materials & Design, 51: 131–135. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes. 2013.04.030. Zhou J T, Yao Z J, Chen Y X, et al., 2014. Fabrication and mechanical properties of phenolic foam reinforced with graphene oxide. Polymer Composites, 35(3): 581–586. DOI: 10.1002/pc.22698. -




 下载:
下载:

 WeChat: JournalBandB
WeChat: JournalBandB