Fabrication of Fe/C Composites as Effective Electromagnetic Wave Absorber by Carbonization of Pre-magnetized Natural Wood Fibers
-
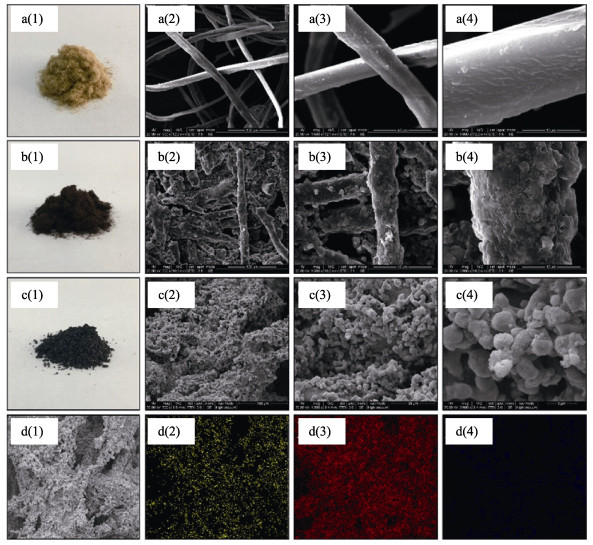
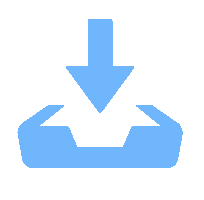
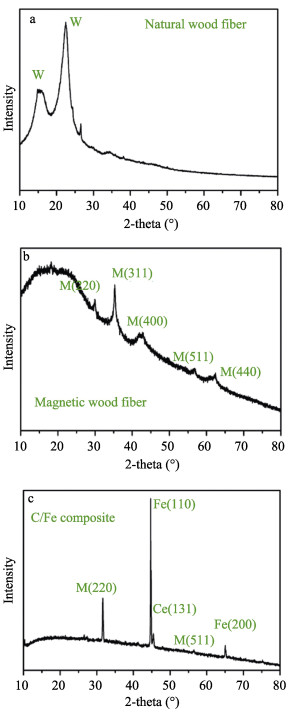
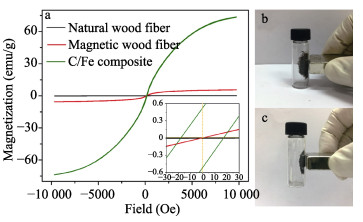
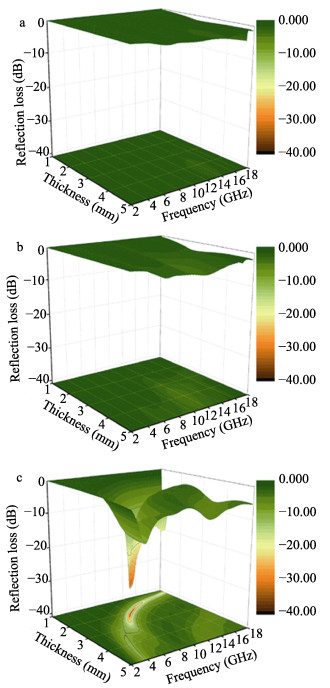
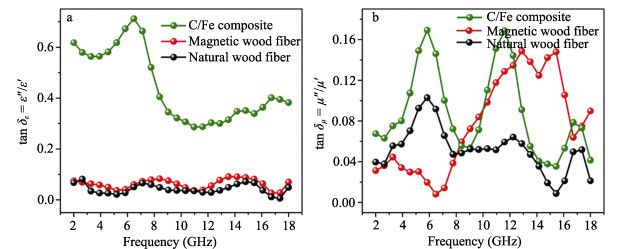
Abstract: With the increasing usage of varied electronic devices, the induced electromagnetic interference (EMI) irradiation pollution has become a novel environmental pollution besides of water and air pollutions, drawing a great of interests from the scientists to address EMW radiation problem via designing various electromagnetic wave (EMW) absorbers, which is supposed to be with lightweight, thin thickness, wide effective absorbing bandwidth and strong absorbing capacity. One kind of the most attractive absorbers is magnetic carbon composites. Here, we successfully synthesized porous structural C/Fe composites by in-situ carbonization of pre-prepared Fe3O4/wood fibers at 1000℃. The EMW absorption property of C/Fe composites is excellent with a minimum RL value of -32.67 dB at 9.86 GHz, a matching thickness of 2.2 mm and a wide response bandwidth of 14.5 GHz. This excellent absorption performance is proved to be due to the continuous network of Fe3O4/Fe/ Fe3C hybrids, permitting optimal impedance matching, the strongest dielectric loss and the optimal magnetic loss. Moreover, the interface polarizations of Fe-Fe3C and Fe3O4-Fe interfaces, are positive to improve the microwave absorption performance.
-
Key words:
- carbonization /
- magnetic bio-char /
- electromagnetic wave absorption /
- cementite /
- composite
-
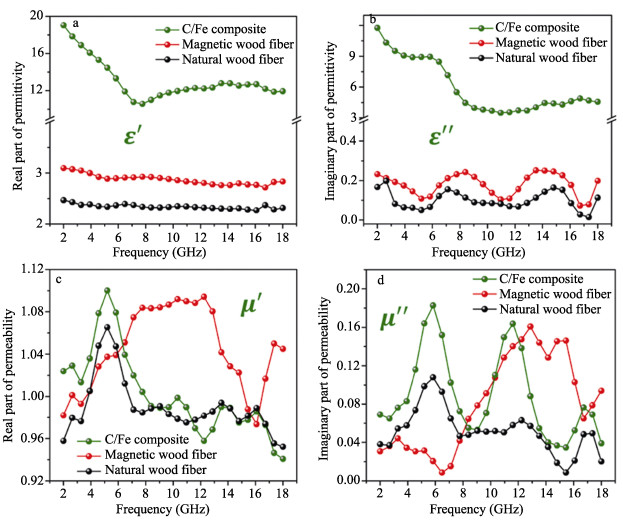
Figure 6. Frequency dependences of real parts (a) and imaginary parts (b) of complex permittivities of natural wood fibers, magnetized wood fibers and C/Fe composites; Frequency dependences of real parts (c) and imaginary parts (d) of complex permeabilities of natural wood fibers, magnetized wood fibers and C/Fe composites
-
Cave I D, 1997. Theory of X-ray measurement of microfibril angle in wood. Wood Science and Technology, 31(3): 143–152. DOI: 10.1007/BF00705881. El-Rahaiby S K, Rao Y K, 1979. The kinetics of reduction of iron oxides at moderate temperatures. Metallurgical Transactions B, 10(2): 257–269. DOI: 10.1007/bf02652470. He C N, Wu S, Zhao N Q, et al., 2013. Carbon-encapsulated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a high-rate lithium ion battery anode material. ACS Nano, 7(5): 4459–4469. DOI: 10.1021/nn401059h. Jian X, Xiao X Y, Deng L J, et al., 2018. Heterostructured nanorings of Fe-Fe3O4@C hybrid with enhanced microwave absorption performance. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10(11): 9369–9378. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b18324. Jiang J J, Li X J, Han Z, et al., 2014. Disorder-modulated microwave absorption properties of carbon-coated FeCo nanocapsules. Journal of Applied Physics, 115(17): 17A514. DOI: 10.1063/1.4865461. Jiang W J, Gu L, Li L, et al., 2016. Understanding the high activity of Fe-N-C electrocatalysts in oxygen reduction: Fe/Fe3C nanoparticles boost the activity of Fe-Nx. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 138(10): 3570–3578. DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b00757. Li G, Xie T S, Yang S L, et al., 2012. Microwave absorption enhancement of porous carbon fibers compared with carbon nanofibers. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 116(16): 9196–9201. DOI: 10.1021/jp300050u. Li J S, Duan Y, Lu W B, et al., 2018. Polyaniline-stabilized electromagnetic wave absorption composites of reduced graphene oxide on magnetic carbon nanotube film. Nanotechnology, 29(15): 155201. DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/ aaac72. Li W X, Lv B, Wang L C, et al., 2014. Fabrication of Fe3O4@C core–shell nanotubes and their application as a lightweight microwave absorbent. RSC Advance, 4(99): 55738–55744. DOI: 10.1039/c4ra10172c. Liu X G, Ou Z Q, Geng D Y, et al., 2010. Influence of a graphite shell on the thermal and electromagnetic characteristics of FeNi nanoparticles. Carbon, 48(3): 891–897. DOI: 10.1016/ j.carbon.2012.09.052. Lou Z C, Han H, Zhou M, et al., 2018a. Synthesis of magnetic wood with excellent and tunable electromagnetic wave-absorbing properties by a facile Vacuum/Pressure impregnation method. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6(1): 1000–1008. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng. 7b03332. Lou Z C, Li Y J, Han H, et al., 2018b. Synthesis of porous 3D Fe/C composites from waste wood with tunable and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 6(11): 15598–15607. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng. 8b04045. Lou Z C, Zhang Y, Zhou M, et al., 2018c. Synthesis of magnetic wood fiber board and corresponding multi-layer magnetic composite board, with electromagnetic wave absorbing properties. Nanomaterials, 8(6): 441. DOI: 10.3390/nano8060441. Lv H, Guo Y H, Yang Z H, et al., 2017. A brief introduction to the fabrication and synthesis of graphene based composites for the realization of electromagnetic absorbing materials. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 5(3): 491–512. DOI: 10.1039/c6tc03026b. Lv H, Liang X H, Ji G B, et al., 2015. Porous three-dimensional flower-like Co/CoO and its excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7(18): 9776–9783. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b01654. Obi Reddy K, Uma Maheswari C, Shukla M, et al., 2013. Tensile and structural characterization of alkali treated Borassus fruit fine fibers. Composites Part B: Engineering, 44(1): 433–438. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.04.075. Oka H, Hojo A, Seki K, et al., 2002. Wood construction and magnetic characteristics of impregnated type magnetic wood. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 239(1/2/3): 617–619. DOI: 10.1016/s0304-8853(01)00684-9. Qiang R, Du Y C, Wang Y, et al., 2016. Rational design of yolk-shell C@C microspheres for the effective enhancement in microwave absorption. Carbon, 98: 599–606. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.11.054. Quan B, Liang X H, Zhang X, et al., 2018. Functionalized carbon nanofibers enabling stable and flexible absorbers with effective microwave response at low thickness. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10(48): 41535–41543. DOI: 10.1021/ acsami.8b16088. Su L W, Zhong Y R, Zhou Z, 2013. Role of transition metal nanoparticles in the extra lithium storage capacity of transition metal oxides: a case study of hierarchical core-shell Fe3O4@C and Fe@C microspheres. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 1(47): 15158. DOI: 10.1039/c3ta13233a. Vestal C R, Zhang Z J, 2002. Atom transfer radical polymerization synthesis and magnetic characterization of MnFe2O4/Polystyrene Core/Shell nanoparticles. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 124(48): 14312–14313. DOI: 10.1021/ja0274709. Wang X L, Huang X, Chen Z R, et al., 2015. Ferromagnetic hierarchical carbon nanofiber bundles derived from natural collagen fibers: truly lightweight and high-performance microwave absorption materials. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 3(39): 10146–10153. DOI: 10.1039/c5tc02689j. Wu G L, Cheng Y H, Xie Q, et al., 2015. Facile synthesis of urchin-like ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Materials Letters, 144: 157–160. DOI:10.1016/j.matlet. 2015.01.024. Wu H J, Wu G L, Ren Y Y, et al., 2015. Co2+ /Co3+ ratio dependence of electromagnetic wave absorption in hierarchical NiCo2O4-CoNiO2 hybrids. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 3(29): 7677–7690. DOI: 10.1039/c5tc01716e. Xiang J, Li J L, Zhang X H, et al., 2014. Magnetic carbon nanofibers containing uniformly dispersed Fe/Co/Ni nanoparticles as stable and high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2(40): 16905–16914. DOI: 10.1039/c4ta03732d. Xu H L, Yin X W, Zhu M, et al., 2017. Carbon hollow microspheres with a designable mesoporous shell for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 9(7): 6332–6341. DOI: 10.1021/acsami. 6b15826. Zhao B, Shao G, Fan B B, et al., 2015. Investigation of the electromagnetic absorption properties of Ni@TiO2 and Ni@SiO2 composite microspheres with core-shell structure. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 17(4): 2531–2539. DOI:10. 1039/c4cp05031b. Zhao S C, Gao Z, Chen C Q, et al., 2016. Alternate nonmagnetic and magnetic multilayer nanofilms deposited on carbon nanocoils by atomic layer deposition to tune microwave absorption property. Carbon, 98: 196–203. DOI: 10.1016/ j.carbon.2015.10.101. -



 下载:
下载:

 WeChat: JournalBandB
WeChat: JournalBandB